In this Cisco CCNA tutorial, we’re going to cover troubleshooting at Layer 1 and Layer 2 of the OSI stack. Scroll down for the video and also text tutorial.
Cisco Basic Layer 1 and 2 Troubleshooting Video Tutorial

Aelina Anne Cherian

Hi Neil, just wanted to tell you that I cleared the CCNA exam today!! So happy and so grateful for all your lectures and all your help. Thank you so much sir!
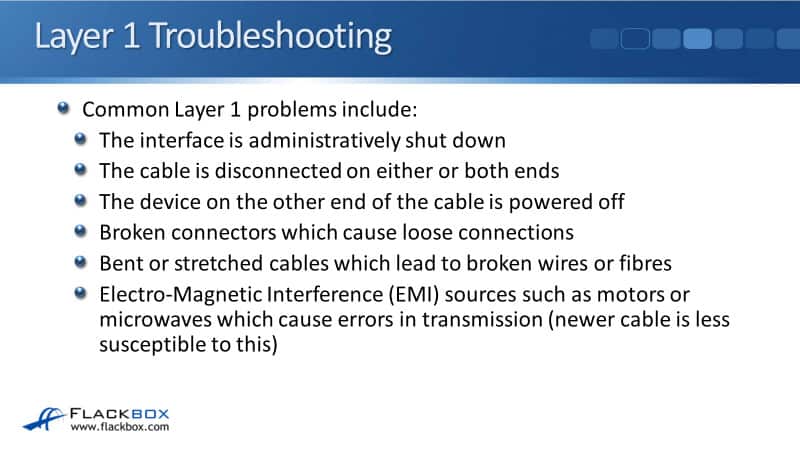
Layer 1 Troubleshooting
First thing, our copper and fibre cables are liable to break if not handled correctly. Treat cables correctly. Don't bundle them up and wrap them up together because you're liable to break them if you do that. You'll see it happening quite a lot in the real world.

Some common Layer 1 problems include the interface is administratively shut down. On switches, interfaces are up by default, but administrators can manually shut them down. It's actually best practice to shut down unused interfaces to stop users from plugging devices in there.
On routers, interfaces are shut down by default. If you configure an interface on a router, remember to do the no-shutdown command.
If the cable is disconnected on one or on both ends, then obviously, you're not going to have any traffic going through there. Also, if a device on the other end of the cable is powered off, then you're not going to have any traffic going through there either.
Broken connectors can cause loose connections and this happens quite commonly as well. On an Ethernet cable, the RJ45 connector with the clip on the end, it's quite easy for that to get broken off. Therefore, there isn't anything to retain it in the interface it's plugged into, and it's easy for it to get a loose connection that way. Also, bent or stretched cables can break the internal wires or fibers.
Lastly, Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) sources such as motors or microwaves can cause errors in transmission. That is not such a big problem if you've got a newer cable. CAT7 has got much better shielding than CAT3 cable does.
Layer 1 Troubleshooting Commands
A useful command for troubleshooting at Layer 1 is:
show ip interface brief
When you enter the command, it will show you the status of the interface. If it shows "administratively down," that means you haven't entered the ‘no shutdown’ command. So, enter that command to bring the interface up.
If it shows "down/down," that means that the administrator has done a ‘no shutdown’ on the interface, but there's a Layer 1 issue. So, check that it is cabled in at both ends and that the device on the other side is powered on. If a device on the other side is powered off, or if you don't have a cable securely connected on both sides, the interface will show as "down/down."

The last setting you can have there for the status in a ‘show ip interface brief’ is "up/down." That typically indicates a Layer 2 issue or a speed mismatch. In this case, check if the interface configuration is the same on both sides of the link. A common issue would be if you've got different VLAN settings on both sides of the link.
Show ip interface brief
Below is an example output of ‘show ip interface brief’. You can see that FastEthernet0/1 is up/up, so that is all good. FastEthernet0/2 is administratively down, so you need to do a ‘no shutdown’ on the interface to bring it up.

FastEthernet0/2 is down/down, indicating most likely a Layer 1 problem. Check that it's cabled on both sides and powered on the other side. FastEthernet0/2 is up/down, which most likely is a configuration mismatch between this device and the device on the other side for those interfaces. So, go on both devices, do a ‘show run’ and check the configuration on both interfaces.
Show Interface
The next command is ‘show interface’. If interfaces are reporting an excessive amount of errors, it could be either a Layer 1 or a Layer 2 problem. Check the integrity of the cable and check if there are no problems with the cable. Again, check your administrative configuration matches on both sides of the link.

Here’s an example of a ‘show interface’ command. If you enter the command and hit enter, you'll get a really long output because it'll show you the command for every single interface in the router or switch.
Usually, we'll do a ‘show interface’ and then specify interface like we've done here for FastEthernet0/2. We can see that it's set to full-duplex and the speed is 100Mb/s. We've got no input errors and no output errors, so that's a good sign.

Speed and Duplex Mismatches
A possible error you can have is speed and/or duplex mismatches on your interfaces. If you've got incorrect speed settings, that can cause the interface to operate below its maximum speed.
For example, if one side is set to auto and the other side is set manual, or if both sides are set to auto, and it doesn't manage to negotiate correctly, that can cause an incorrect speed setting where it's going to run below the optimal speed.
If you've got a speed mismatch where you've manually configured the speed on both sides of the link, that will typically bring the interface down. If you've got a duplex mismatch, an interface will typically stay up but you'll get terrible performance because you'll have loads of collisions on the interface.
If you do a ‘show interface’ command, that will typically report a really high number of errors in that case which would give you a clue to what the problem is.

Again, both sides of the link must be set the same for the speed and duplex. Either set both sides to auto or manually configure both sides. Now, you don't need to do that for all ports.
For example, in one switch, maybe port 1 is set manually, and the device on the other side has to be set manually. It could be that port 2 is set auto, then, the device on the other side of that link should also be set to auto.
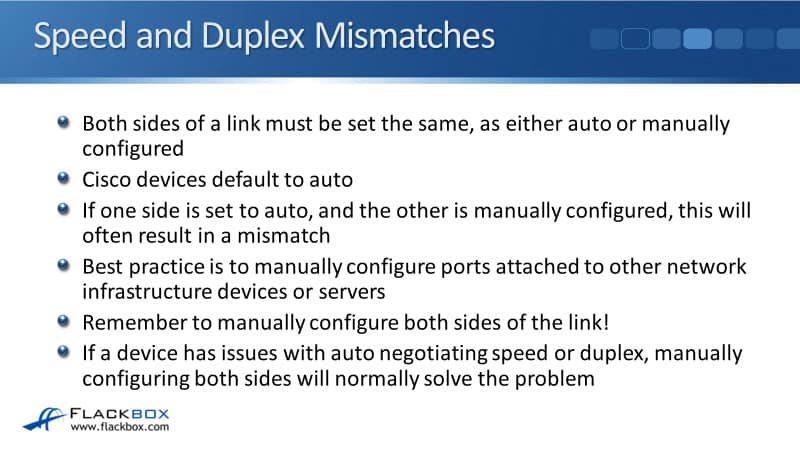
Your Cisco devices will default to auto. If one side is set to auto and the other is manually configured, it will often result in a mismatch, so always set them both the same. Best practice is to manually configure ports attached to other network infrastructure devices or servers.
So, your drivers, your switches, your firewalls, et cetera, have those configured manually, also your servers. For your normal PCs, we'll typically leave that set to auto. Again, remember if you do configure it manually, do both sides of the link.
If a device has issues with auto-negotiating speed or duplex, then manually configuring both sides will normally solve that problem. If you do have a duplex mismatch, then CDP, Cisco Discovery Protocol, should detect that and it'll log it as you see in the example below. We've got a duplex mismatch discovered on FastEthernet0/0 (not half duplex).

Cisco Basic Layer 1 and 2 Troubleshooting Configuration Example
This configuration example is taken from my free ‘Cisco CCNA Lab Guide’ which includes over 350 pages of lab exercises and full instructions to set up the lab for free on your laptop.
Click here to download your free Cisco CCNA Lab Guide.

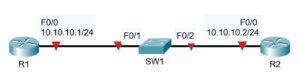
- Verify the status of the switch port connected to R2 with the show ip interface brief It should show status and protocol up/up.
SW1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 10.10.10.10 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset up up
2. Shut down the interface connected to R2 and issue a show ip interface brief command again. The status and protocol should show administratively down/down.
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/2
SW1(config-if)#shutdown
*Mar 1 00:44:34.212: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to administratively down
*Mar 1 00:44:35.219: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
SW1(config-if)#do show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 10.10.10.10 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
3. Bring the interface up again. Verify the speed and duplex setting.
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/2
SW1(config-if)#no shutdown
SW1(config-if)#
*Mar 1 00:45:52.637: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
*Mar 1 00:45:53.644: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
SW1#sh interface f0/2
FastEthernet0/2 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Lance, address is 00e0.8fd6.8902 (bia 00e0.8fd6.8902)
BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
4. Set the duplex to half on Switch 1. Leave the settings as they are on R2.
SW1(config-if)#duplex half
SW1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
5. Verify the state of the interface.
The interface is down/down. It will not forward traffic.
SW1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES manual down down
6. Set the duplex back to full duplex.
SW1(config)#int f0/2
SW1(config-if)#duplex full
SW1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
7. Set the speed to 10 Mbps.
SW1(config)#int f0/2
SW1(config-if)#speed 10
SW1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
8. Check if the interface is still operational.
SW1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 10.10.10.10 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
The interface status is down/down.
9. Check if the interface is operational on R2. What is the status of the interface?
R2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 10.10.10.2 YES manual up down
The interface status is up/down on R2.
Additional Resources
What Is Network Troubleshooting?: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/what-is-network-troubleshooting.html
Network Troubleshooting Methodology and Techniques: https://study-ccna.com/network-troubleshooting-methodology-techniques/
Configuring and Troubleshooting Ethernet 10/100/1000Mb Half/Full Duplex Auto-Negotiation: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/ethernet/10561-3.html
Libby Teofilo

Text by Libby Teofilo, Technical Writer at www.flackbox.com
Libby’s passion for technology drives her to constantly learn and share her insights. When she’s not immersed in the tech world, she’s either lost in a good book with a cup of coffee or out exploring on her next adventure. Always curious, always inspired.