In this Cisco CCNA training tutorial, you’ll learn about VLAN Access ports and how to configure them. Access ports are configured on switch interfaces where end hosts such as desktop PCs are plugged in. Scroll down for the video and also text tutorial.
VLAN Access Ports Video Tutorial

Eugene Ochieng

I want to say THANK YOU for the course. It was really helpful in attaining the Cisco CCNA 200-301 certification.
An access port carries traffic for one specific VLAN. For example, when an Engineering PC is plugged in to a switch, the port where it is connected to will be configured as an access port for the Engineering VLAN.
The configuration is all on the switch. The end host doesn't need to know anything about VLANs.
You can pass your CCNA exam at the first attempt by taking my Cisco CCNA Complete course in conjunction with the AlphaPrep test engine.
VLANs segment the Campus LAN into smaller broadcast segments by only allowing traffic within the same VLAN. Traffic between VLANs must go via a router.
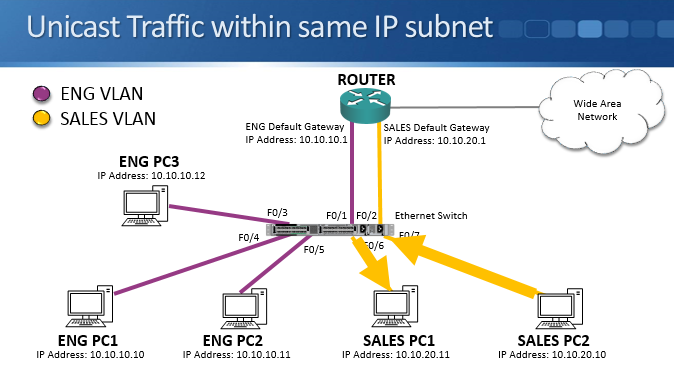
Unicast Traffic within the Same IP Subnet
We have an Engineering VLAN and a Sales VLAN in the example above.
There is usually a one-to-one relationship between an IP subnet and a VLAN. In our example the Engineering PCs are in IP subnet 10.10.10.0/24 and the Eng VLAN, and the Sales PCs are in IP subnet 10.10.20.0/24 and the Sales VLAN.
All Engineering PCs and the router interface in the Engineering IP subnet (‘ENG Default Gateway’) go into the Engineering VLAN. All Sales PCs and the router interface for the Sales subnet (‘SALES Default Gateway’) go into the Sales VLAN.
Whenever a host sends traffic, the switch will learn the host’s MAC address and the port that MAC address is reachable through. For example if Sales PC1 has MAC address 1111.2222.3333 and is connected to interface FastEthernet 0/6, as soon as it sends any traffic the switch will learn that 1111.2222.3333 is reachable via FastEthernet 0/6.
Whenever unicast traffic is sent within the same IP subnet and VLAN, the switch will send it out only the port which the destination host is connected to. For example when Sales PC2 sends to Sales PC1, the switch will forward it out only port FastEthernet 0/6 if it has already learned the MAC address of Sales PC1.
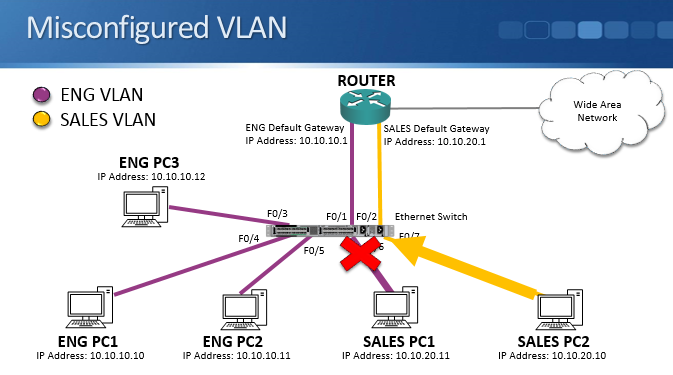
Misconfigured VLAN Example
If we misconfigured VLANs, for example if we accidentally put Sales PC1 in the Engineering VLAN instead of the Sales VLAN, the other PCs won’t be able to communicate with it, even if they’re in the same IP subnet. The switch doesn’t forward traffic between different VLANs. So if Sales PC2 at 10.10.20.10 sends traffic to Sales PC1 at 10.10.20.11 but they’re in different VLANs, it won’t make it to the destination.
You have to be careful when configuring VLANs. Remember, hosts which are in the same IP subnet should be in the same VLAN.
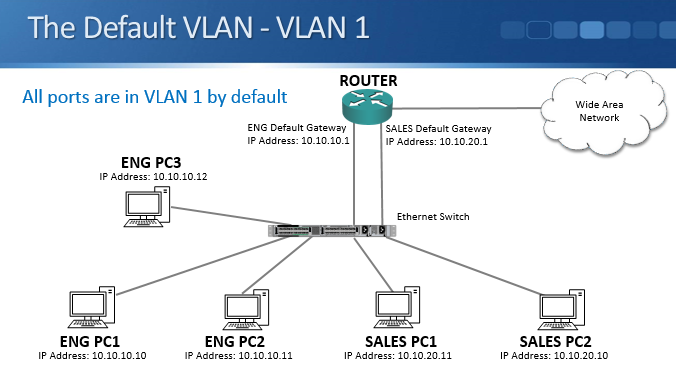
The Default VLAN – VLAN 1
VLAN1 is the default VLAN, all ports on the switch are in this VLAN by default. Until you manually configure VLANs, your Campus LAN is one big broadcast domain.
This isn’t a good idea as it affects performance and security, so you should configure specific VLANs.
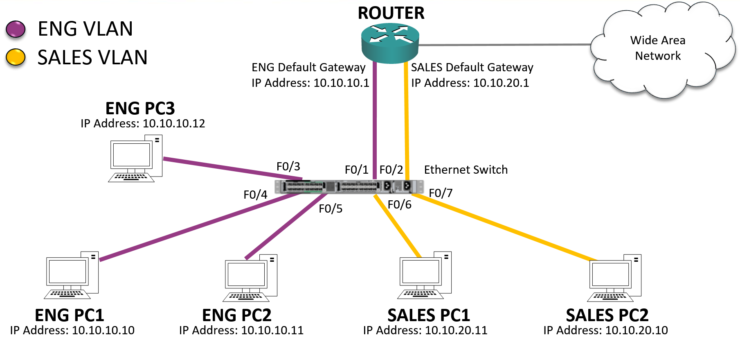
VLAN Access Ports Configuration Example
Using the same example above, the Engineering PCs are connected to interfaces FastEthernet 0/3, 0/4 and 0/5, and 0/6. We also need to put the router interfaces in the correct VLAN, so FastEthernet 0/1 goes in the Engineering VLAN too.
Interfaces FastEthernet 0/2, 0/6 and 0/7 go in the Sales VLAN.
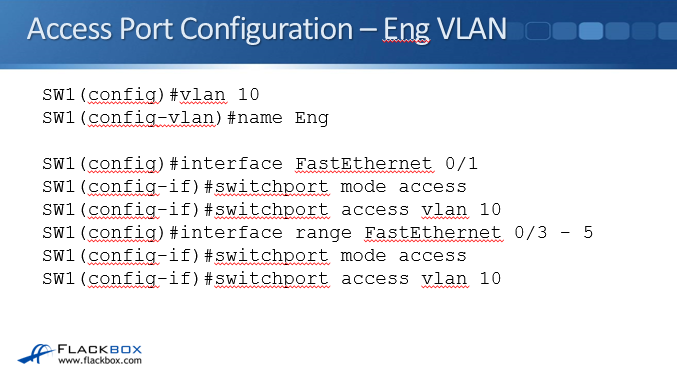
VLAN Access Port Configuration – Eng VLAN
Let’s configure the Engineering VLAN first. First off, we have to create the VLAN and to do that, the command is simply ‘VLAN’ and then the number you want to use for this VLAN. You do not need to number your VLANs sequentially 1,2,3 etc. You can give them any number you like so it’s common to relate the VLAN number to the IP subnet somehow, for example using VLAN 10 for IP subnet 10.10.10.0/24 and VLAN 20 for IP subnet 10.10.20.0/24.
At global config, type VLAN 10. That gets us into the VLAN sub-configuration. Optionally, you can give it a name and it’s a good idea to give it a descriptive name here. Here we've called it Eng, type ‘name ENG’.
Next, we need to configure our switch ports as access ports in the correct VLAN. Type interface FastEthernet 0/1, then switchport mode access and switchport access vlan 10.
If you are wondering about the other types of ports, aside from access ports we have trunk ports. We will cover those in the next post.
Next we need to put interfaces FastEthernet 0/3 - 0/5 in to the Eng VLAN. Rather than having to do these same commands over and over again for each individual port, we can configure a range of ports. Type interface range FastEthernet 0/3 – 5. You have to do this in exactly this syntax or you will receive an error message.
Then we type switchport mode access and switchport access vlan 10 again. Now we have completed configuring our Engineering VLAN.
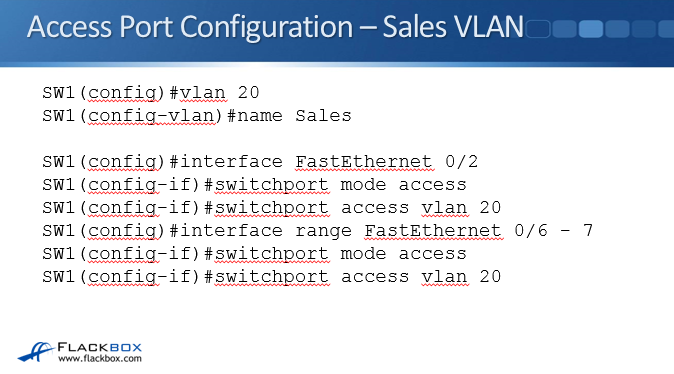
VLAN Access Port Configuration – Sales VLAN
Now let’s configure the Sales VLAN using vlan 20. Just like we did with Engineering VLAN, we will name our VLAN to Sales. So at the global config, type vlan 20 then name Sales.
Next type interface FastEthernet 0/2 then switchport mode access and switchport access vlan 20.
To configure the range, type interface range FastEthernet 0/6 – 7 then switchport mode access and switchport access vlan 20 again.
VLAN Access Port Verification Commands – Show VLAN Brief
To verify your configuration, type show vlan brief. It will show all the VLANs available on the switch along with the ports associated with each VLAN. So you will see interfaces FastEthernet 0/1, 0/3, 0/4 and 0/5 are in the Eng VLAN 10 and FastEthernet 0/2, 0/6 and 0/7 are in the Sales VLAN 20.
All of the other ports are in the default VLAN 1.
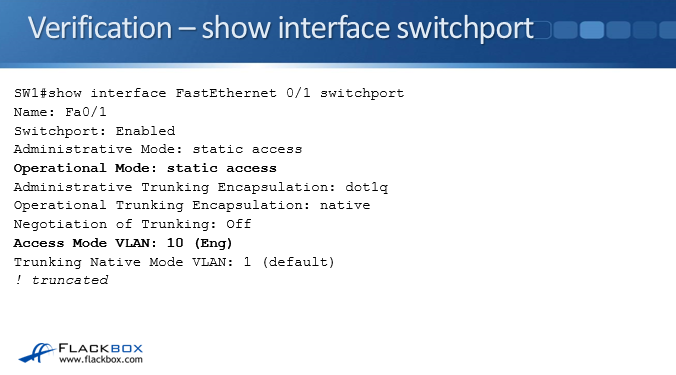
VLAN Access Port Verification Commands – Show Interface Switchport
‘Show VLAN Brief’ shows you global information about all your VLANs and all of your ports. If you want to see information specific to an individual port, type show interface FastEthernet 0/1 switchport, referencing the port you’re interested in. In the example above, you can see that it's an access port in VLAN 10, which is the Engineering VLAN.
Additional Resources
Understanding and Configuring VLANs from Cisco