In this NetApp training tutorial, I’ll give you an overview of the NetApp platforms that run on the Element operating system, namely SolidFire and NetApp HCI. Scroll down for the video and also text tutorial.
NetApp Element OS Platform Overview Video Tutorial – SolidFire and NetApp HCI

Brad Dyke

I saw the writing on the wall about new technologies and wanted to transition to a new role as a storage / HCI cloud architect.
I used Flackbox.com classes to sync me up with ONTAP and passed my certs two days after completing your training, it took about six business days in total.
I got the job I wanted with CGI and it’s a great company to work for.
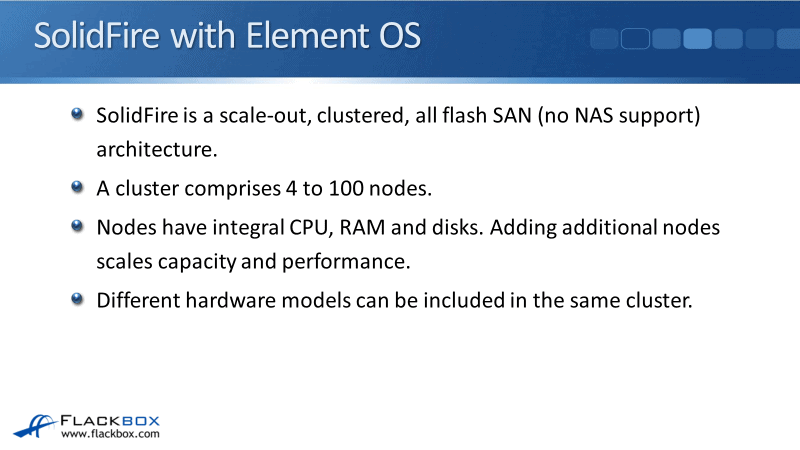
Solid Fire with Element OS
SolidFire is a scale-out, clustered, all flash SAN, and no NAS support architecture. SolidFire is all SSDs and it has no hybrid option to support spinning discs.
SolidFire system’s cluster can have 4 to 100 nodes. The nodes have an integral CPU, RAM, and discs. Unlike FAS and AFF systems with ONTAP, and the E and EF series systems, SolidFire don't have external disc shelves. The disc comes from the same chassis instead.
Adding additional nodes means adding an entire chassis. Doing that adds capacity and performance to the entire cluster. Just like with all of the other systems, different hardware models can be included in the same cluster.
Each node provides a fixed amount of IOPS performance, so it makes it easy to plan your performance. Capacity and performance are pooled across the entire cluster and managed separately. The administrator sets the capacity and required performance when creating a volume.
Whenever you've got a new workload that needs to be supported with the SolidFire system, it's very easy to provision the capacity on the performance for that particular workload. Unlike, with a lot of other systems, managing your capacity in your performance is being decoupled or managed separately.
RAID is not used on SolidFire systems. It has a system called SolidFire Helix that writes a copy of the data to two nodes. Now, if you're thinking that it’s the same as RAID 1 Mirroring, it's not. With RAID 1, the discs are in the same chassis. If you lose that chassis, then you've lost all of your data unless you have a backup, of course.
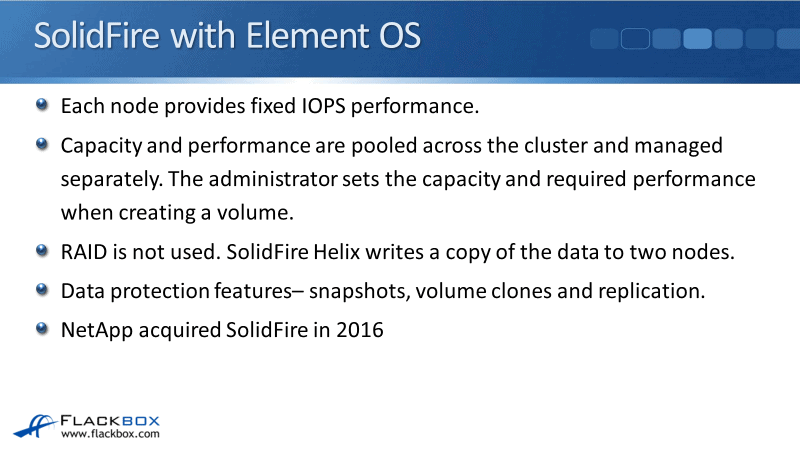
SolidFire Helix gives you better redundancy because it's mirroring the discs. Those discs are in different systems. Therefore, if you lose the node, it is still on the other node and it's still available in the cluster.
SolidFire also has data protection features, which are snapshots, volume clones, and replication. SolidFire was an acquisition by NetApp in 2016.
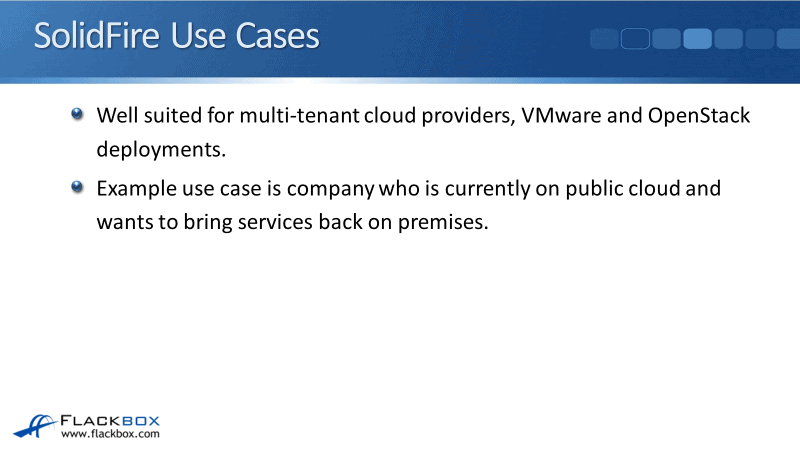
SolidFire Use Cases
SolidFire is well known for having advised QoS capabilities and its cluster supports many varied workloads. You can control the minimum and maximum levels of performance measured in IOPS at the volume level. Controlling the performance for your different workloads is a very advanced feature, but is simple to manage.
The system is designed for simple administration, orchestration, and automation. Administrators do not need to be storage specialists. If you've got a virtualization engineer who's used to working with VMware systems for example, then they can easily provision the storage for all systems without being an expert in storage.

The features of SolidFire tend to lend itself to the actual use cases. It is well-suited for multi-tenant cloud providers. It can be either on public cloud or private cloud running VMware, OpenStack, etc.
An example use case is a company that is currently got their workloads deployed in the public cloud, but they want to pull that back in on premises, SolidFire would be an excellent choice for that.
SolidFire
Here's what SolidFire looks like, let's have a look at this on the NetApp website. We go to the main netapp.com homepage and click on products. SolidFire is all flash so we will find it under the all flash menu.

We can also see the different models that are currently for sale. Again, by the time you see this tutorial, there might be more updated models available so you can come to the products page to see those.
All of the current models support 100,000 IOPS per node. The difference between them is the effective capacity you get on those different models.
NetApp HCI
With SolidFire, the capacity, and the performance are pooled across the entire cluster. Similar to our HCI methodology, but SolidFire systems provide storage only.
SolidFire doesn't provide compute all into one system as you'll get with an HCI system. NetApp HCI provides both storage and compute in a scaled-out pooled infrastructure.

With NetApp HCI, the storage nodes run on SolidFire Element OS, the same as our SolidFire systems. The compute nodes run on VMware OS.
The blades are placed in the NetApp HCI chassis, or you can buy the entire nodes as one system. Those nodes can either be the compute node running VMware or the storage node running Element OS.
A cluster supports 2 to 64 compute nodes and 4 to 40 storage nodes. You need to have both compute and storage nodes in the system. A cluster can be deployed in under 30 minutes easily and simply using the NetApp Deployment Engine (NDE).
The cluster is designed to be managed through VMware vSphere web client with storage plugins. Single pane of glass to manage the entire system, simple administration.
The use of separate dedicated nodes allows storage and compute to be scaled independently of each other. In the first generation of HCI systems that came out, it was complained that you would need to buy a node that had both compute and storage.
Therefore, whenever you wanted to scale out, you could scale out easily. However, you are scaling out both of the compute and the storage at the same rate.
What if you needed more compute, but not more storage? Or what if you needed more storage, but not more compute? Then, you couldn't do that. But you can do it with NetApp HCI because you've got separate compute and storage nodes.
Now, due to that reason, some analysts have argued that NetApp HCI is converged rather than hyper-converged infrastructure. They are alike in terms of being separate storage and compute infrastructures even though they are all in the same system.
Since then, NetApp HCI has been rebranded as NetApp Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure instead of hyper-converged infrastructure. NetApp took that criticism on board and they changed what the HCI stands for.
NetApp HCI Use Cases
NetApp HCI adds VMware compute capability to the SolidFire storage and Element OS. Similar to SolidFire, it is using the same operating system. It just adds that compute capability on the one single system.
NetApp HCI shares similar use cases with SolidFire. It's got simple administration for workload consolidation. You can run multiple different workloads on there and manage them as very simple as you would expect from an HCI system.
It's well-suited for public or private multi-tenant cloud providers. The Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) with VMware View is used for the compute.
NetApp HCI
This is what NetApp HCI looks like. In the datasheet for NetApp HCI which you can get from the NetApp website, you can see the different nodes in there.

We've got the H610S storage node which can be used for SolidFire system as well as NetApp HCI. The H610C graphic compute node has GPU cards, so it's good for graphics-intensive workloads. Then we've got H410C compute node and there are different GPU capability options to choose from.
H410C is half width, so two of these nodes can fit in the same physical chassis. That's why in the datasheet, you’ll see that the cores are double what you see on the physical cores.
You can also see information on the storage nodes. It states how much capacity is supported and how many IOPS are supported per node.
Additional Resources
NetApp HCI Overview: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/hci-solutions/hcvdivds_netapp_hci_overview.html
NetApp HCI or SolidFire: Which One Is Right for You?: https://www.netapp.com/blog/netapp-hci-or-solidfire/
Click Here to get my 'NetApp ONTAP 9 Storage Complete' training course.
Libby Teofilo

Text by Libby Teofilo, Technical Writer at www.flackbox.com
Libby’s passion for technology drives her to constantly learn and share her insights. When she’s not immersed in the tech world, she’s either lost in a good book with a cup of coffee or out exploring on her next adventure. Always curious, always inspired.