In this Cisco CCNA tutorial, you’ll learn about interface speed and duplex. Scroll down for the video and also the text tutorial.
Cisco Speed and Duplex Settings Video Tutorial

Thomas Napier

Thanks for your training. I passed the CCNA by watching your video tutorials and using Alphaprep. 2 months ago I didn’t know what a switch was. Now I can’t wait to start my career in the IT field.
Interface Speed and Duplex
Interface speed and duplex are set to ‘auto’ by default. So both sides of a link should auto-negotiate to full duplex and the fastest available speed. They should do that automatically. The default is ‘auto’ on Cisco devices.
Best practice is to manually set the speed and duplex on ports connected to another network infrastructure device, such as a router, a switch, a firewall, or a server. Because if you set it manually, that is just a little bit more reliable.
To be honest though, ‘auto’ should work just fine as well. In a normal building, you’ll maybe have hundreds or even thousands of PCs, so you’re not going to configure the speed and duplex for all of those manually. But you’ll have less amount of network infrastructure devices and servers, and best practice is to set the speed and duplex on there manually.
It’s very important to set matching speed and duplex settings on both sides of the link. So, either leave both sides set as auto or set both sides manually. Do not have one side at ‘auto’ and the other side set manually.

For example, if you’ve got the server plugged into the switch, you could go on to the switch, and you could manually set the speed and duplex on there. If you’re not sure how to do it on the server, maybe you would just leave it on the server to ‘auto.’ That would be a big mistake, okay?
You either have to set it to manual on both sides or auto on both sides. If you set it to manual on one side and ‘auto’ on the other, then that will often cause speed and duplex issues, which can bring the link down or lead to terrible performance on the link. So, always do it the same on both sides, that’s important.
Let’s have a look at the commands to do that. At the interface level, duplex is either full or half, and then speed is the speed of the interface. So let’s do that in the lab. I’m already in the interface configuration on my switch. I will set the 'duplex full'. This is a fast ethernet link, so I’ll set it to 'speed 100'.
Notice when I do that, it will bring the interface down, and then it will bring it back up again. Right now, I haven’t configured this on the router. So it’s ‘auto’ on one side and manual and the other. I don’t want that, so I will go on to the router, and it’s already in the interface configuration as well.
I’ll also set 'speed 100' and 'duplex full' on this side. That was all the things we want to do for our initial configuration.

Verification Commands
After we’ve done that, we want to verify that everything is working as expected. The first command here is ‘show running-config,’ which will show the entire configuration on the switch. It’s very common to use this command, either just to see what’s happening on a switch or for troubleshooting later.
I’ll go back to the enabled prompt because it’s a show command, and I can enter just the shortened version, ‘show run.’ It will print out the entire running configuration on this switch for me, and I can hit the space bar to scroll down a page at a time. If I want to break out, I can hit Ctrl+C.
The next command on the slide was ‘show ip interface brief.’ Between ‘show run’ and ‘show ip interface brief,’ these are the two most common commands that you will run on a router or a switch. If you’re working as a professional network engineer, it’s typical that you will run both of those commands multiple times every day.
So, ‘show run’ shows the entire configuration, ‘show ip interface brief’ shows you the status of your interfaces and which IP address is configured on which interface. Again, if you jump onto a router or a switch and you’re gathering information about it, this is a very common command to use.

I can see in the example here that interface FastEthernet0/0 has got IP address 192.168.0.1 on there. The status is up, and the protocol is up. Interface FastEthernet0/1 is administratively down, which means I have not done a ‘no shutdown’ on that interface. So, that was on the router.
I can also do the same command on the switch as well. So I do a ‘show ip interface brief,’ I’m going to get a longer output here because it’s on a switch now. There are more interfaces on there. But, again, it’s exactly the same output.
I can see all of my interfaces that are on the device and the IP addresses that are configured on those interfaces as well. This is a layer two switch, so it’s just got the Vlan1 interface right now with an IP address on there. I can also see the status of my interfaces.
Next verification command, I can do a ‘show run interface vlan 1.’ On the switch again, if I do a ‘show run,’ it shows the entire configuration. This can be really long. So, if you want to just check the configuration for a particular interface, you can do a ‘show run interface.’
For example, interface FastEthernet0/1, you see it there as I’m scrolling through this ‘show run’ config. To get straight to it, I could do a ‘show run interface fastethernet0/1,’ and it just shows me that part of the configuration.
A ‘show run interface’ shows you the configuration you’ve manually configured on the interface. If you do a ‘show interface fastethernet0/1,’ that will show you the MAC address on the interface, the IP address on the interface if one is configured, and it also shows you traffic statistics as well.
If you think there’s maybe an issue with an interface, this is a useful command for troubleshooting that. It also will verify if traffic is passing through the interface or not as well. You see an example here, we’ve had 571 packets output, and 97 packets inputs of traffic is going through that interface.
This command will also show you if you have any errors on the interface as well. So right now, we’ve got zero input errors and zero output errors, so that is all good.
The last command issue here is a ‘show version.’ That will show you the version of IOS, the operating system that is running on this switch or router. I’ll do a ‘show version,’ and I can see the version of IOS that is running on the switch. It’ll also give me some additional information in there as well like how much memory is installed in the device.
Cisco Speed and Duplex Settings Configuration Example
This configuration example is taken from my free ‘Cisco CCNA Lab Guide’ which includes over 350 pages of lab exercises and full instructions to set up the lab for free on your laptop.
Click here to download your free Cisco CCNA Lab Guide.
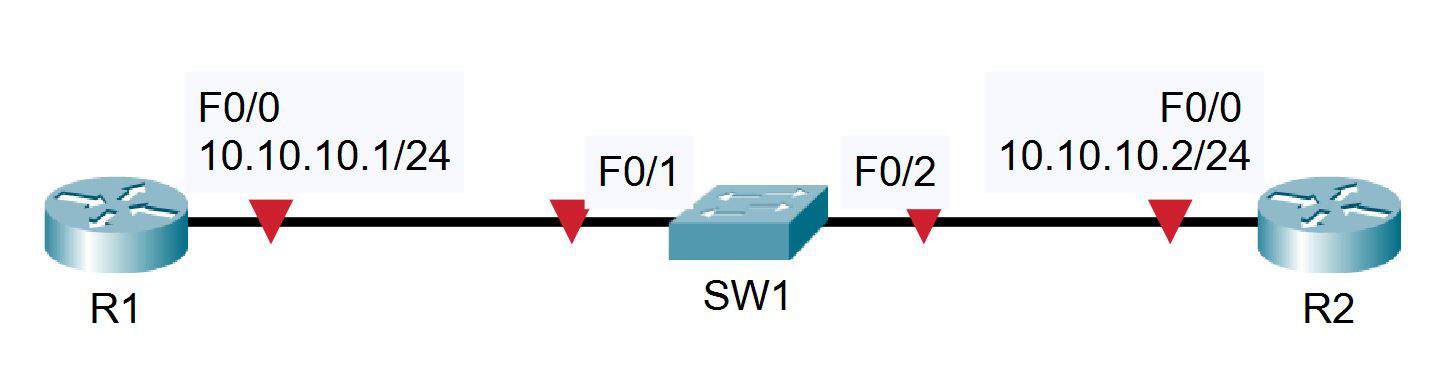
- Verify the status of the switch port connected to R2 with the show ip interface brief command. It should show status and protocol up/up.
SW1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 10.10.10.10 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset up up
2. Shut down the interface connected to R2 and issue a show ip interface brief command again. The status and protocol should show administratively down/down.
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/2
SW1(config-if)#shutdown
*Mar 1 00:44:34.212: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to administratively down
*Mar 1 00:44:35.219: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
SW1(config-if)#do show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 10.10.10.10 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
3. Bring the interface up again. Verify the speed and duplex setting.
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/2
SW1(config-if)#no shutdown
SW1(config-if)#
*Mar 1 00:45:52.637: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
*Mar 1 00:45:53.644: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
SW1#sh interface f0/2
FastEthernet0/2 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is Lance, address is 00e0.8fd6.8902 (bia 00e0.8fd6.8902)
BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
4. Set the duplex to half on Switch 1. Leave the settings as they are on R2.
SW1(config-if)#duplex half
SW1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
5. Verify the state of the interface.
The interface is down/down. It will not forward traffic.
SW1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES manual down down
6. Set the duplex back to full duplex.
SW1(config)#int f0/2
SW1(config-if)#duplex full
SW1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up
7. Set the speed to 10 Mbps.
SW1(config)#int f0/2
SW1(config-if)#speed 10
SW1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to down
8. Check if the interface is still operational.
SW1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 10.10.10.10 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
The interface status is down/down.
9. Check if the interface is operational on R2. What is the status of the interface?
R2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 10.10.10.2 YES manual up down
The interface status is up/down on R2.
Additional Resources
Configure Speed and Duplex: https://study-ccna.com/configure-speed-and-duplex/
Configuring and Troubleshooting Ethernet 10/100/1000Mb Half/Full Duplex Auto-Negotiation: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/ethernet/10561-3.html
Cisco Networking Academy's Introduction to Basic Switching Concepts and Configuration: https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2181836&seqNum=5#
Libby Teofilo

Text by Libby Teofilo, Technical Writer at www.flackbox.com
Libby’s passion for technology drives her to constantly learn and share her insights. When she’s not immersed in the tech world, she’s either lost in a good book with a cup of coffee or out exploring on her next adventure. Always curious, always inspired.